Most of the Caribbean nations have adopted a single plan to solicit from former slaving nations an apology, more aid and damages for 300 years of slavery, which they say have hobbled their economies and public health
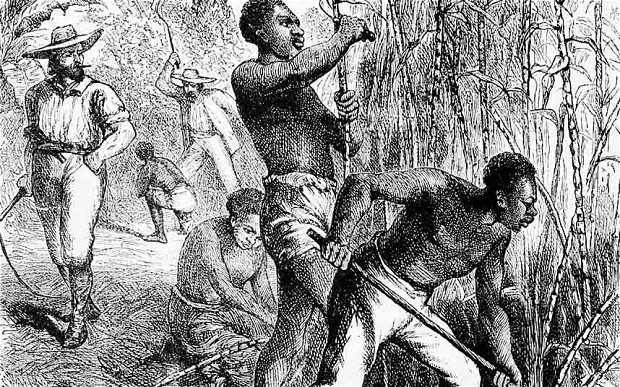
By Philip Sherwell, New York
A coalition of Caribbean countries has unveiled its demands for reparations from Britain and other European nations for the enduring legacy of the slave trade.
The leaders of 15 states adopted a wide-ranging plan, including seeking a formal apology from former colonial powers, debt cancellation, greater development aid as well as unspecified financial damages for the persisting “psychological trauma” from the days of plantation slavery.
The series of demands to be made of former slaving nations such as Britain, France, Spain, Portugal and The Netherlands were agreed at a closed-door meeting of the Caribbean Community (Caricom) in St Vincent and the Grenadines.
The Atlantic slave trade took place from the 16th through to the 19th centuries.
The group hired Leigh Day, the British law firm, to push their claims after the company secured a £20 million compensation award for Kenyans who were tortured by colonial authorities during the Mau Mau rebellion in the 1950s.
The reparations debate has long simmered in the Caribbean where many blame slavery for modern ills, ranging from economic weakness to health epidemics such as diabetes and hyper-tension allegedly caused by their ancestors’ poor diets.
Caricom is pushing for increased technological assistance as it says European powers shackled the region during the world’s industrialisation by confining it to producing and exporting raw materials such as sugar.
The plan also demands an increase of aid for public health and educational and cultural institutions such as museums and research centres.
And it calls for the creation of a “repatriation programmes” to help resettle members of the Rastafarian movement in Africa. Repatriation to Africa has long been a central belief of Rastafarians.
Martin Day, of Leigh Day, said he would request a meeting with European officials to seek a negotiated settlement, but would pursue a legal complaint if Caribbean nations are not satisfied with the outcome of any talks.
It has been 180 years since Britain abolished slavery but the demand for an unqualified apology remains as controversial as the calls for financial damages.
In 2007, Tony Blair, the then prime minister, expressed “deep sorrow and regret” for the “unbearable suffering” caused by Britain’s role in slavery but stopped short of a formal apology. His words angered many in the Caribbean as inadequate and resonating of legal caution.
The British government, which currently contributes about £15million a year in development to the Caribbean, said that it has not been presented with the demands, but has consistently signalled opposition to financial reparations.
“The UK has been clear that we deplore the human suffering caused by slavery and the slave trade,” a Foreign Office spokesman said. “However we do not see reparations as the answer. Instead, we should concentrate on identifying ways forward with a focus on the shared global challenges that face our countries in the twenty-first century.”
But Professor Verene Shepherd, the chairman of Jamaica’s reparations committee, told The Daily Telegraph last month that British colonisers had “disfigured the Caribbean”, and that their descendants should now pay to repair the damage.
“If you commit a crime against humanity, you are bound to make amends,” she said. “The planters were given compensation, but not one cent went to the freed Jamaicans”.
The Caricom nations highlighted the region’s enduring troubles as well the suffering of the victims of the trade in humanity and the profits made by the slaving powers.
“The transatlantic slave trade is the largest forced migration in human history and has no parallel in terms of man’s inhumanity to man,” their claim reads. “This trade in enchained bodies was a highly successful commercial business for the nations of Europe.”
www.telegraph.co.uk, 11 Mar 2014
