Middle East & Africa
-
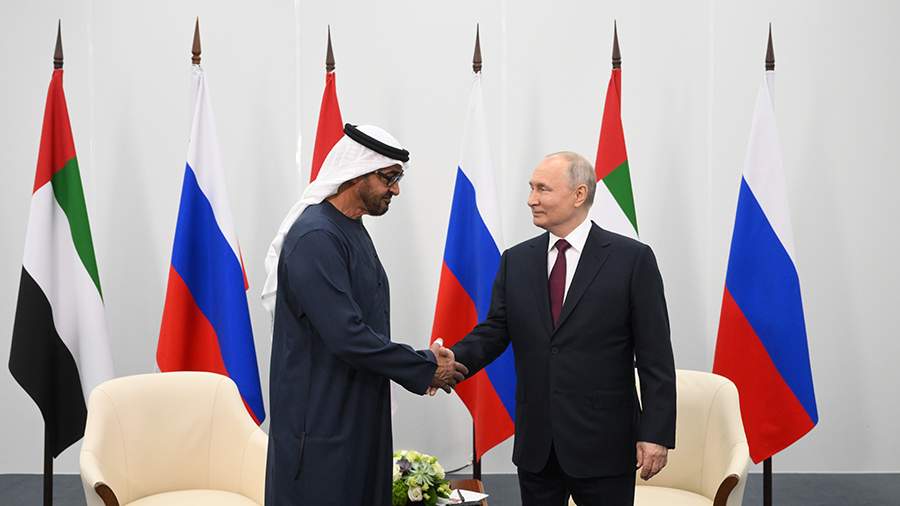

Russia develops long-term ties with UAE and Turkey in a highly polarized world
Russia’s largest economic forum (SPIEF) held in St. Petersburg on June,14 – June, 17 has resulted in strengthening ties with the two strategic partners – […]
-

Do all Turks and Iranians want secularism, and why?
in IranI can’t speak about Iran, because it’s mostly very closed society, at least when you look from outside. But when I have travelled over there, […]
-

Why didn’t Arabs revolt against Ottoman Empire over the course of Ottoman Rule?
in Middle EastThere are several reasons why the Arabs did not revolt against the Ottoman Empire over the course of its rule. One reason is that the […]
-

The Effectiveness of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Regime
in IranAmong the international security regimes, the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Regime has a prominent rank due to the destructive power of the nuclear weapons over regional and […]
-
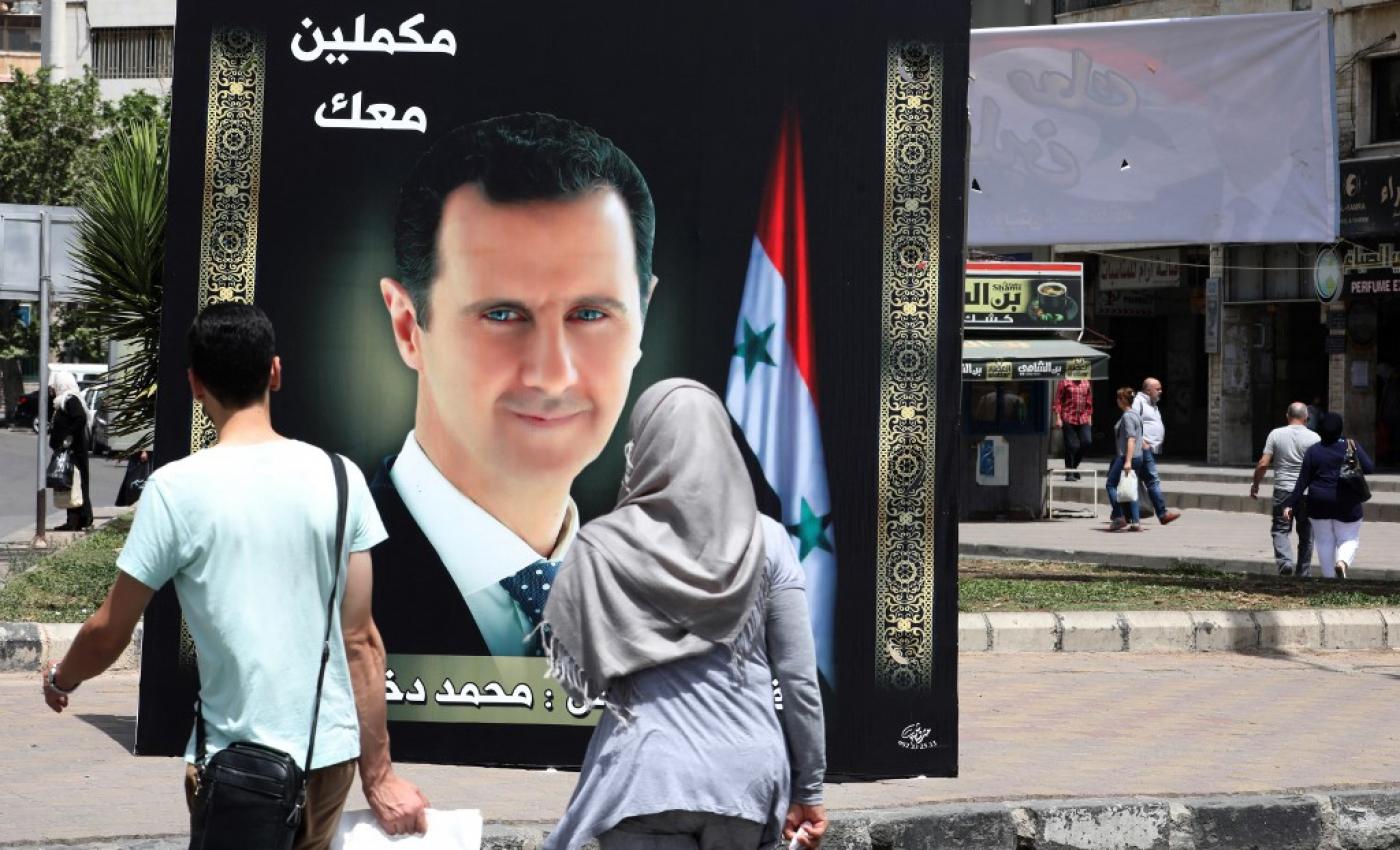

Assad has won 4th term, what’s next?
Syrian President Bashar al-Assad was re-elected for the 4th term in office with 95.1% of the votes. According to Assad’s government, the election results proved […]
-
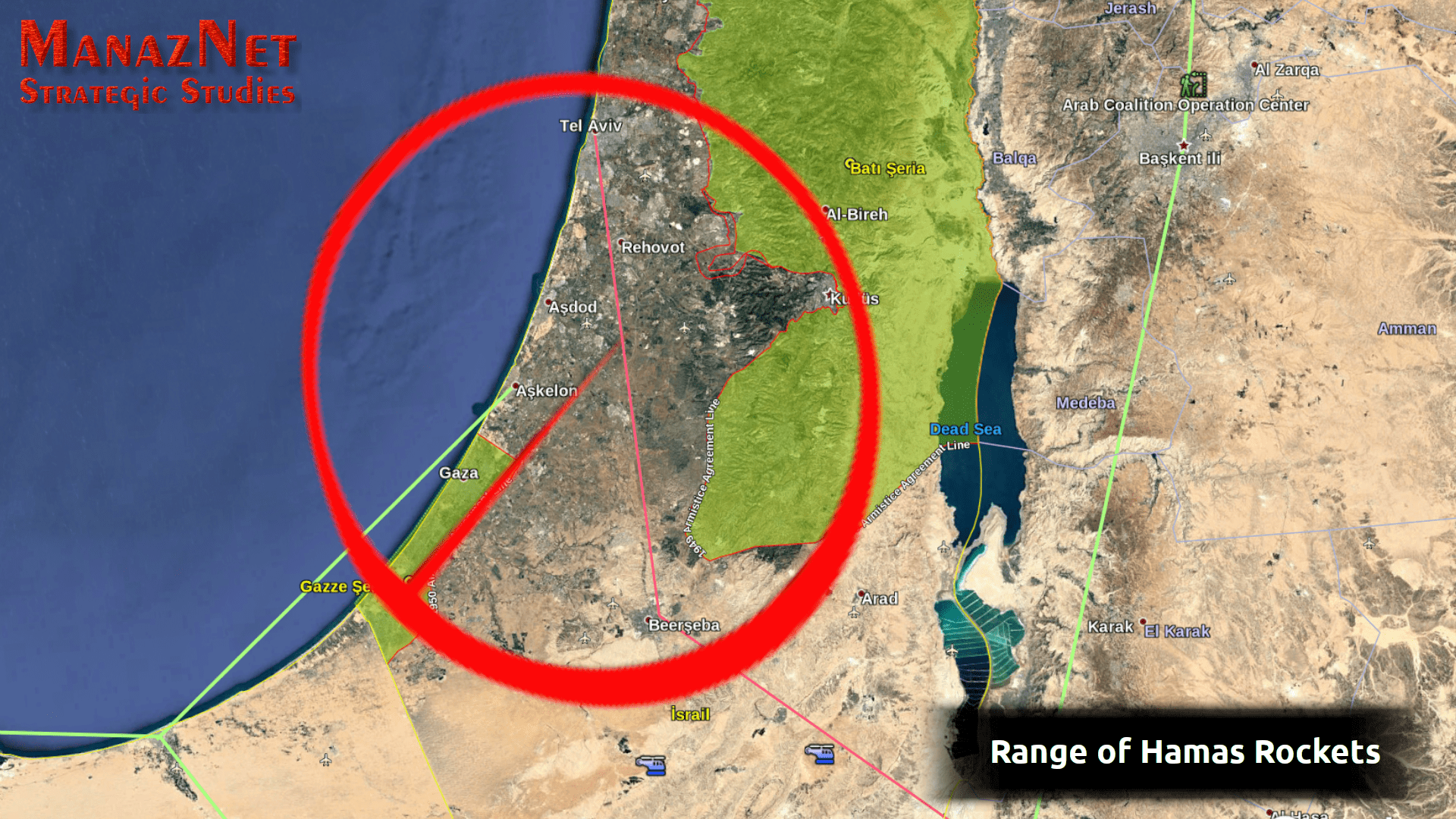
Netanyahu’s Last Battle
Dr. Abdullah Manaz : The MiddleEast Analyst The most important development in the last Palestine & Israel war was the results of opinion polls regarding […]
-
Russia develops long-term ties with UAE and Turkey in a highly polarized world
-
Do all Turks and Iranians want secularism, and why?
-
Why didn’t Arabs revolt against Ottoman Empire over the course of Ottoman Rule?
-
The Effectiveness of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Regime
-
Assad has won 4th term, what’s next?
-
Netanyahu’s Last Battle
